Diamond Buying Guide
jetha bhai zaveriDiamond Anatomy & Cut Quality
In order to protect our clients, we at Jetha Bhai Zaveri guarantee that all of our diamonds meet our strict and demanding standards, based upon our long history and experience. Not only that, we also provide CONSULTANCY SERVICES for any one intending to purchase a diamond from anywhere. Consultancy provided by Dr. Vimal Bhai, who was in the panel of the Bureau of Indian Standards which formulated the Indian Standard for the Grading of Polished Diamonds.
Understanding the 4 C’s of Diamonds Shopping
Each diamond is unique on its own just as our fingerprints, hence no two diamonds are alike in all respects, the reason for the differences in their value which only a gemmologist or an expert can judge. Nonetheless, the basic 4 C’s ( Colour, Clarity, Cut & Carat) of the diamond when examined under 10X magnification are a must and we highlight the same.
Clarity
One of the key measures of a diamonds overall quality is its Clarity. Flawless diamonds are extremely rare to find.
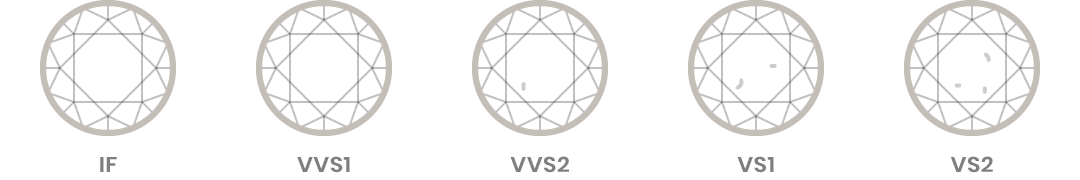
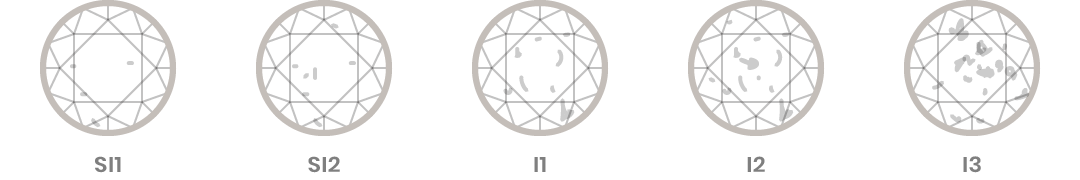
Diamond Clarity Descriptions
The diamond is ‘Flawless’ (FL) , if under 10X magnification, no inclusions like ‘cloud’, ‘pinpoints’, etc are seen. These diamonds are free from internal characteristics/inclusions and external characteristics/blemishes under 10X magnification. As Nature would bless almost all diamonds with natural blemishes called ‘inclusions,’ these clarity short comings are not easily caught by the untrained eye. It takes years of study and practical experience in order to become an expert on judging the diamonds. The clarity grades begin from ‘Flawless to I3. The Flawless diamonds have been described above.
The ‘Internally Flawless’ (IF) diamond are free from internal characteristics/inclusions and only possess external characteristics/inclusions when examined under 10X magnification.
The ‘Very Very Slightly ‘ (VVS) included diamonds contain minute internal inclusions which are easily caught by an expert’s eye.
The ‘Very Slightly’ (VS) included diamonds contain minor internal characteristics/inclusions.
The ‘Slightly Included ‘ (SI) diamonds contain noticeable internal characteristics/inclusions and are easy to observe.
The ‘Included ’ (I1,I2,I3) diamonds contain prominent internal characteristics / inclusions. These inclusions are clearly visible face up to the naked eye. As the inclusions grow from prominent to very prominent to extremely prominent they scale down from I1 to I3. These inclusions distinctly reduce the brilliance of the diamond.
Cut
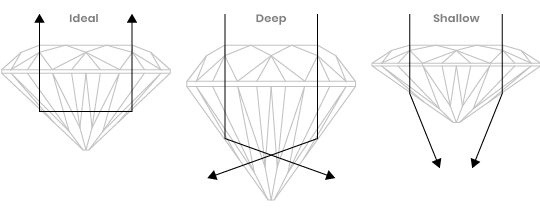
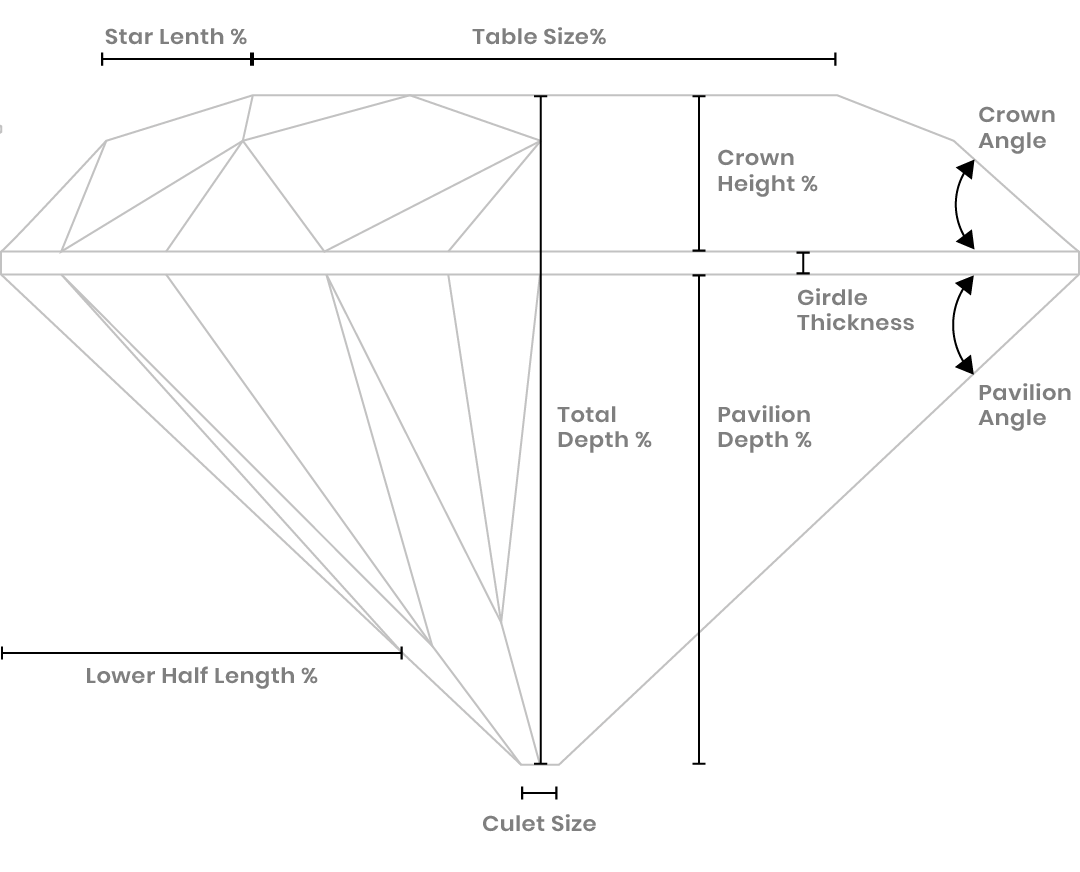
The ‘Cut’ of a diamond refers to its facets. The facets that give the diamond all its charisma. The art of the highly skilled master cutter of the diamond is to proportionately cut the rough gemstone with facets in such a manner that it expels its full magnificence and shows its beauty. The ace cutter could shape the rough diamond into various shapes, Round, being the most popular. Some of the other shapes are the Pear Shape (Drop Shape), Heart Shape, Oval, Marquise (Boat Shape) , Emerald (Rectangular/ Octagonal Shape) , Princess (Square Shape). The complexity of the cut of a diamond lies in the proportions, finish and the final polish.
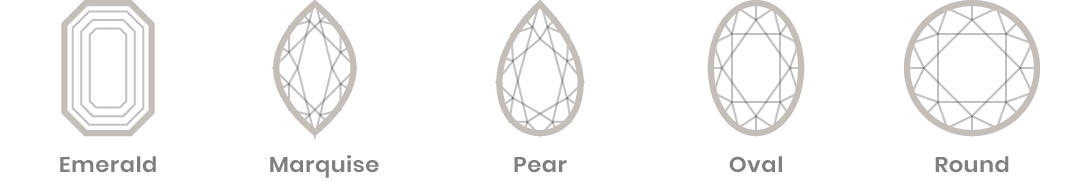
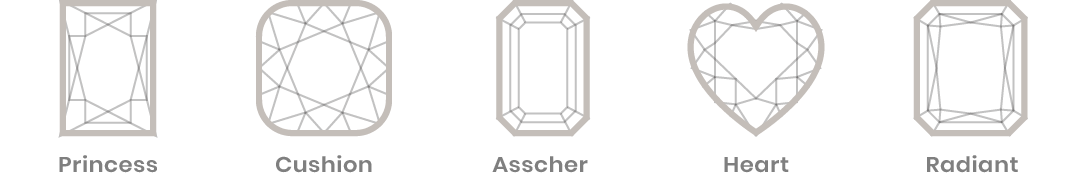
Color
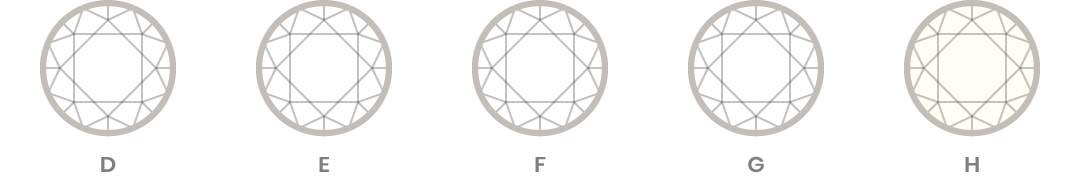
In nature, the absence of any colour is extremely rare as most diamonds carry tiny amounts of nitrogen. Anything picture perfect in Nature is rare. Even our skins are not cent per cent perfect in all respects. For a common person it is pretty difficult to detect the minute variations of colour, but these distinctions would be credential in the value of the diamond due to its rarity. The Colour of the diamond is scaled running from ‘D’ ( colourless ) to ‘Z’ ( saturated ). In general terms the scale represents Colourless to Yellow, Brown and Grey. However, there are diamonds which also surpass the ‘Z’ grade ! They are darker in tone and or higher in saturation than the ‘Z’ colour diamond and may possess other noticeable hues or tones. These are the Fancy Diamonds or the Coloured Diamonds. It is pertinent to note here that the Fancy Diamonds are very valuable and hence are graded with another set of different parameters.
Carat (Size)
Unlike the Karat which signifies the unit for the purity of gold, the Carat is a weight measure for the diamond. A carat is equivalent to 0.2 grams and is the unit of weight for diamonds or gemstones. Keeping other factors constant, as the weight of the diamond increase, so does its value. This value increases in an exponential manner. For example a two carat diamond will be worth much more than two times of a one carat diamond of the same quality. High quality large diamonds are extremely rare and are valued to reflect that rarity.